All you have to know about Green Architecture!!
Green building has become more of a necessity than a luxury in recent times. The reason for this is to perform the sustainable development. The Concept of Green Architecture, also known as “sustainable architecture” or “green building,” is the theory, science and style of buildings designed and constructed in accordance with environmentally friendly principles.
Green architecture strives to minimize the number of resources consumed in the building’s construction, use and operation, as well as curtailing the harm done to the environment through the emission, pollution and waste of its components.
PRINCIPLES OF GREEN BUILDING DESIGN
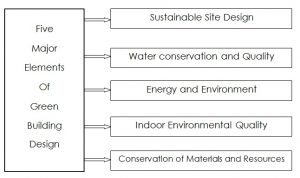
The following points summarize key principles, strategies and technologies which are associated with the five major elements of green building design:
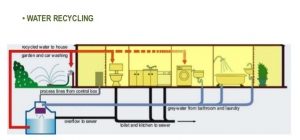
- Water Systems
Water – often called the source of life – can be captured, stored, filtered, and reused. It provides a valuable resource to be celebrated in the process of green building design.
The Green Building Design introduces methods of rainwater harvesting, grey water systems, and living pools. The protection and conservation of water throughout the life of a building may be accomplished by designing for dual plumbing that recycles water in toilet flushing or by using water for washing of the cars. Waste-water may be minimized by utilizing water conserving fixtures such as ultra-low flush toilets and low-flow shower heads. Bidets help eliminate the use of toilet paper, reducing sewer traffic and increasing possibilities of re-using water on-site.
2. Natural Building
A natural building involves a range of building systems and materials that place major emphasis on sustainability. The basis of natural building is the need to lessen the environmental impact of buildings and other supporting systems, without sacrificing comfort or health. To be more sustainable, natural building uses primarily abundantly available, renewable, reused or recycled materials. The use of rapidly renewable materials is increasingly a focus. In addition to relying on natural building materials, the emphasis on the architectural design is heightened. The orientation of a building, the utilization of local climate and site conditions, the emphasis on natural ventilation through design, fundamentally lessen operational costs and positively impact the environmental.

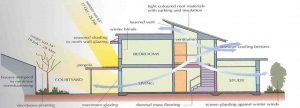
3. Passive Solar Design
Passive solar design refers to the use of the sun’s energy for the heating and cooling of living spaces. The building itself or some element of it takes advantage of natural energy characteristics in its materials to absorb and radiate the heat created by exposure to the sun.
Homes in any climate can take advantage of solar energy by incorporating passive solar design features and decreasing carbon dioxide emissions. Even in cold winters, passive solar design can help cut heating costs and increase comfort.
Major Components: Orientation, double glazed windows, window overhangs, thermal storage walls roof, roof painting, Ventilation, evaporation, day lighting, construction material etc.
4. Green Building Materials
Green building materials are generally composed of renewable rather than non-renewable resources and are environmentally responsible because their impacts are considered over the life of the product. In addition, green building materials generally result in reduced maintenance and replacement costs over the life of the building, conserve energy, and improve occupant health and productivity.
Green building materials can be selected by evaluating characteristics such as reused and recycled content, zero or low off-gassing of harmful air emissions, zero or low toxicity, sustainably and rapidly renewable harvested materials, high recyclability, durability, longevity, and local production.
The materials common to many types of natural building are clay and sand. Other materials commonly used in natural building are: earth (as rammed earth or earth bag), wood (cordwood or timber frame/post-and-beam), straw, rice-hulls, bamboo and stone. A wide variety of reused or recycled non-toxic materials are common in natural building, including urbanite (salvaged chunks of used concrete), vehicle windscreens and other recycled glass.

GREEN BUILDING BENEFITS:
Green building is not a simple development trend; it is an approach to building suited to the demands of its time, whose relevance and importance will only continue to increase.
- Comfort:
Because a well-designed passive solar home or building is highly energy efficient, it is free of drafts. Extra sunlight from the south windows makes it more cheerful and pleasant in the winter than a conventional house.
- Economy:
If addressed at the design stage, passive solar construction doesn’t have to cost more than conventional construction, and it can save money on fuel bills.
- Aesthetics:
Passive solar buildings can have a conventional appearance on the outside, and the passive solar features make them bright and pleasant inside.
- Environmentally responsible:
Passive solar homes can significantly cut use of heating fuel and electricity used for lighting. If passive cooling strategies are used in the design, summer air conditioning costs can be reduced as well.
Bibliography:
http://stumpnersbuildingservices.com/passivesolartemp.html
http://www.green-modeling.com/sustainability/list-of-green-building-materials-for-your-house.html
http://hub.politicsnissues.org/hub/prepared?w=1366;rh=http%3a%2f%2fwww%2eproje
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/291419457_Green_Architecture_A_Concept_of_Sustainability

